Denim has been a popular material in many cultures and decades. It can be seen everywhere from luxurious designer windows to fast fashion brands. Traditionally made from denim, Jeans remain one of the most popular fashion items worldwide.

However, the manufacturing of jeans is one of the fashion industry’s biggest carbon footprints. Denim is mainly made from cotton, and a single pair of cotton jeans consumes between 10,000 and 20,000 litres of water along its supply chain. The majority of the water is used to grow the cotton used and all the different garment washing processes are used to finish the final product. Coupled with the high energy consumption and vast chemical usage in various wet processes, denim is one of the least sustainable fabrics, and has arguably been a significant contributor to climate change.
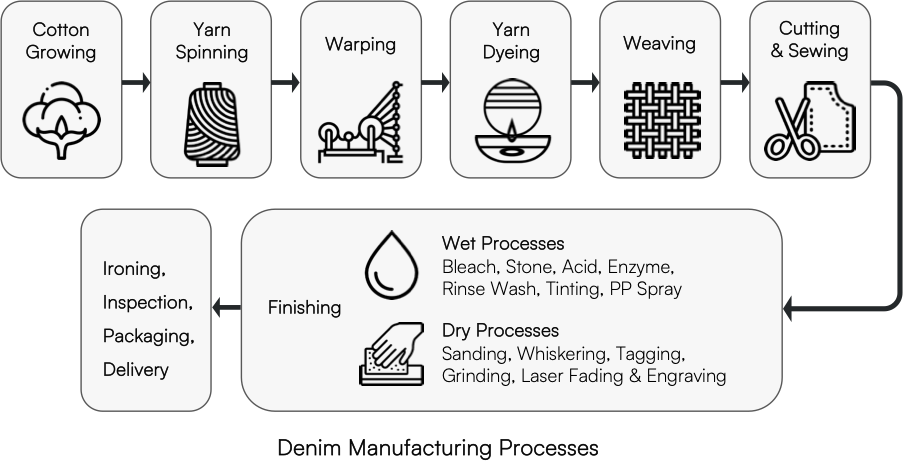
Below, we investigate what options are available to reduce the environmental impact of this supply chain.
What are the more sustainable ways to produce Denim?
Alternative Cotton Use
Since cotton is the primary raw material in denim production, using organic options where no synthetic pesticides or fertilizers are used in the growing process can be a more sustainable way to cultivate it. The farming of organic cotton promotes soil health and biodiversity, and water consumption and chemical usage are minimal. Organic cotton creates 48% less carbon dioxide than conventionally grown cotton and uses around 90% less water. Economically sustainable options, like CmiA, also generally use less chemical pesticides.
Alternative Dyeing Methods
Denim’s traditional dyeing method with indigo dyes is water-intensive and requires a huge amount of sodium hydrosulphite and caustic soda, which are released together with unfixed dyes into water sources.
By using modern dyeing methods, such as pre-reduced indigo, which is water-soluble, the amount of sodium hydrosulphite can be reduced by 60-70%. Newer dyeing methods like Foam Dyeing, where foam is used to transfer indigo dye onto yarns, help to reduce water usage by up to 90% and energy consumption by up to 30%.
Nowadays, natural indigo dyes and fully traceable biosynthetic dyes, which are less toxic for the environment, are available and act as a better alternative to synthetic indigo.

Cationic Denim is a production method where cotton has been chemically modified to be permanently positively charged and can help to reduce water and energy consumption. Due to the positive charge, the cotton absorbs the dye more quickly and results in a reduced dyeing time, chemical usage, and wastewater as a byproduct.
Alternative Finishing Processes
The most energy and water-intensive parts of denim production are the finishing processes, where different types of washes are applied to get special wash-out effects, abrasion level, and hand feel. More sustainable, new technologies are now replacing the traditional ones in these processes.

- Enzymes are used as an alternative to harsh chemicals during bleaching and stone washing. The use of enzymes not only reduces environmental pollution and health hazards but also enhances the quality and texture of fabrics. By using enzymes, only the dye and appearance are changed. The fabric quality, strength and elasticity remain the same.
- Stainless-steel abrasive drums fastened to the washing machine cylinder can reduce water and energy consumption. These drums are specially treated to make them more or less abrasive, depending on the intensity of treatment required. The effect is the same as that of stone-wash and can almost entirely eliminate the carbon footprint of pumice stones.
- Ozone, generated from oxygen, can be used as an alternative bleaching agent to chlorine and potassium permanganate (PP), neither of which are environmentally friendly chemicals. By using ozone for the bleaching process, more than 80% of chemicals and almost 70% of water can be saved compared to the conventional treatment with chlorine bleach.
- Laser engraving technologies are replacing traditional methods like hand-sanding and PP spraying which are unsustainable and may pose hazards to garment workers. By using lasers, less water and chemicals are used and the effects are highly reproducible. Digital design files for laser engraving also make rapid prototyping and adjustment possible.
Even though these new methods still sometimes have to be used in combination with the traditional ones, they help to achieve the same designs and overall look to the denim while saving water, energy, time, and chemicals throughout the process. More advanced technologies and further development of the existing ones are being explored: together they will make denim production even more sustainable.
Follow our LinkedIn page and check out our news channel to learn more about our sustainability initiatives and business updates.

